Raising a healthy child involves paying keen attention to their nutrition. Proper nutrition is pivotal not only for growth but also for cognitive development and preventing various health issues. This comprehensive guide will delve into the essential child nutrition tips every parent needs to know, addressing common concerns and ensuring you’re well-equipped to provide the best for your child.
Understanding the Basics of Child Nutrition
The Importance of Balanced Diets
Children require a variety of nutrients from different food groups. Ensuring a balanced diet that includes fruits, vegetables, grains, protein, and dairy products is crucial. Each food group supplies unique nutrients that are vital in supporting their overall growth and development.
Adequate Caloric Intake
Calories are a measure of energy. Children need a specific amount of energy to grow, play, and learn. However, it’s crucial to balance caloric intake with activity level to prevent obesity — a growing concern in child health.
Key Nutrients and Their Sources
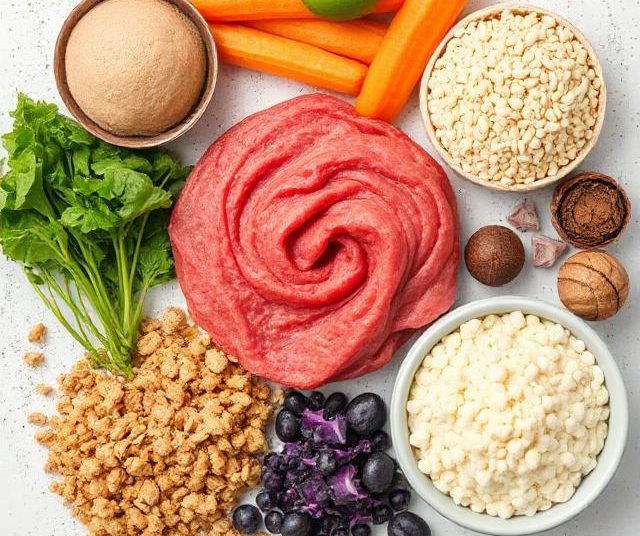

Proteins
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues and are therefore crucial for growing children. Lean meats, eggs, dairy products, nuts, and legumes are excellent protein sources.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary energy source for children. Whole grains, fruits, and vegetables provide not just carbs but also essential fibers and vitamins.
Fats
Healthy fats are crucial for brain development and energy. Sources include fish, nuts, and vegetable oils. It’s advisable to limit unhealthy fats found in fast food and many processed snacks.
Vitamins and Minerals
Each vitamin and mineral plays a crucial role in development. For instance, Vitamin D and calcium are necessary for strong bones, while iron is essential for blood cells. A diverse diet usually covers these nutrients, but in some cases, supplements may be necessary under pediatric guidance.
Age-Specific Nutrition Guidelines
Infants (0-12 months)
Infant nutrition is primarily focused on breastmilk or formula as they provide all the necessary nutrients for the first six months. Introducing solid foods should start around six months of age, initially with pureed fruits and vegetables, and gradually including more variety as the child ages.
Toddlers (1-3 years)
Toddlers need nutrient-dense foods due to their high energy requirements. Focus on whole grains, fruits, vegetables, dairy products, and proteins. Monitor sweet intake to prevent tooth decay and other health issues.
Preschool to School-Age Children (3-12 years)
This age group needs plenty of physical energy and nutrients that support cognitive development. Encourage a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, proteins, and low-fat dairy. Healthy snacks can provide energy between meals.
Common Child Nutrition Concerns

Dealing with Picky Eaters
It’s common for children to go through phases of picky eating. Introducing a variety of foods early can help prevent this. Also, involving children in meal preparation can increase interest in different foods.
Preventing Obesity
Maintaining a balance between calorie intake and physical activity is crucial to prevent childhood obesity. Limiting screen time and encouraging physical play can contribute significantly to maintaining a healthy weight.
Food Allergies and Intolerances
Awareness of potential food allergies is essential. Introduce new foods gradually and monitor for any adverse reactions such as rashes, stomach upset, or breathing difficulties.
Supplementing Child Diet
When to Consider Supplements
Supplements should not replace a balanced diet but can be beneficial in certain circumstances, such as vitamin D deficiencies in areas with low sunlight. Always consult with a pediatrician before starting any supplements.
Choosing the Right Supplements
Select supplements that are age-appropriate and free from harmful additives. Liquid or chewable multivitamins are preferred for younger children who might have difficulty with pills.
Encouraging Healthy Eating Habits
Family Meals
Having regular family meals can encourage healthier eating patterns. It also provides an opportunity for parents to model healthy eating behaviors.
Educating on Nutritional Values
Teaching children about the nutritional value of foods can make them more likely to choose healthier options. Interactive tools like games or charts can make learning fun.
Conclusion
Providing proper nutrition for your child is a dynamic process that adapts as they grow and their needs evolve. By understanding the basics of child nutrition, addressing common concerns, and encouraging healthy eating habits, you can ensure your child receives the necessary nutrients for optimal growth and development. Remember, a healthy child is not just about the right diet but also a happy, active, and well-rounded lifestyle.